
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial
- Ji-Yeon Park, Joonyub Lee, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kyung Wan Min, Kyung Ah Han, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soo Lim, Young-Hyun Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Mook Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, the Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) study investigators
- Received August 7, 2023 Accepted November 30, 2023 Published online April 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0259 [Epub ahead of print]
- 196 View
- 8 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
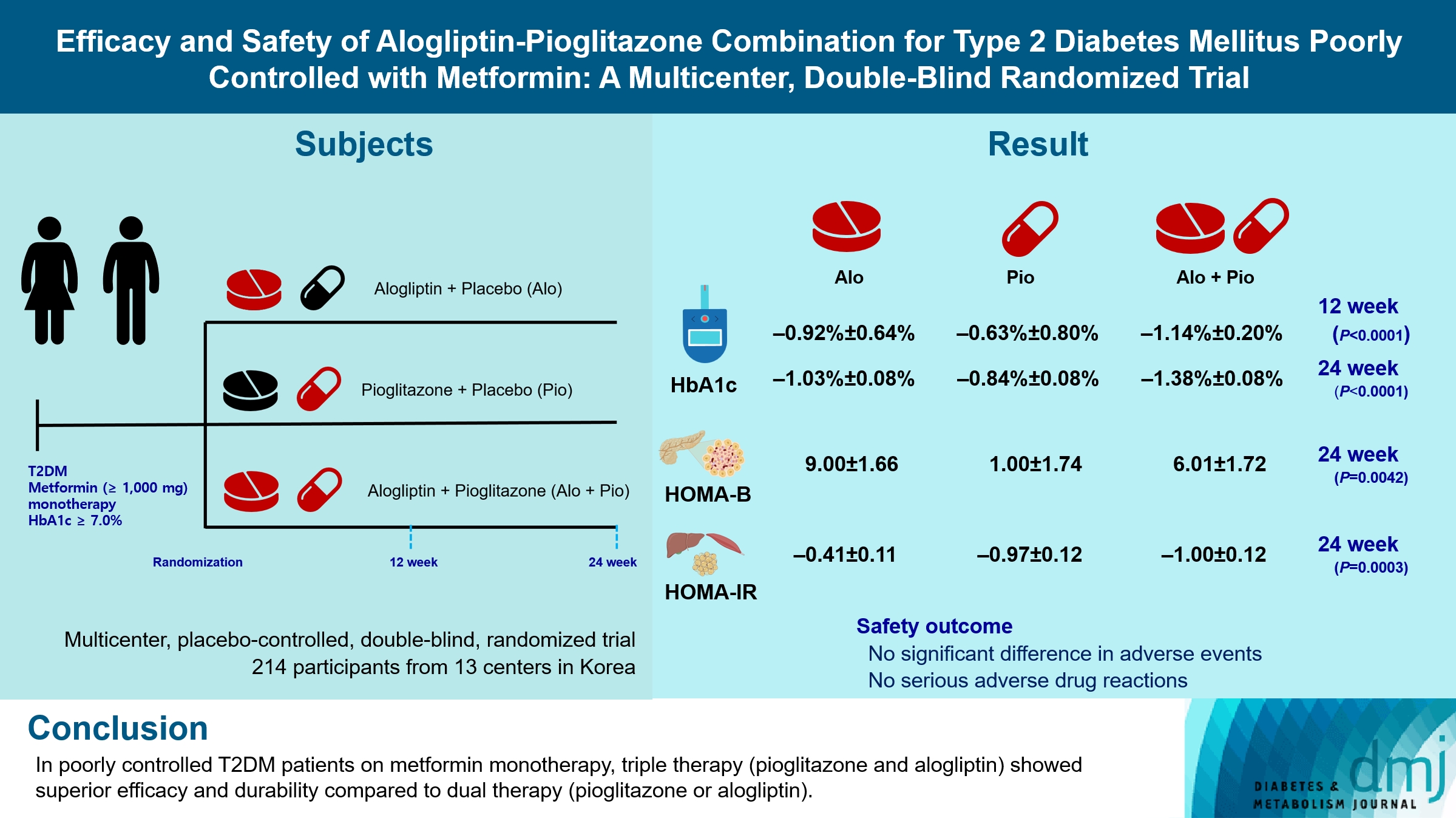
Guidelines for switching to triple combination therapy directly after monotherapy failure are limited. This study investigated the efficacy, long-term sustainability, and safety of either mono or dual add-on therapy using alogliptin and pioglitazone for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who did not achieve their target glycemic range with metformin monotherapy.
Methods
The Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) was a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial. A total of 214 participants were randomized to receive alogliptin+pioglitazone (Alo+Pio group, n=70), alogliptin (Alo group, n=75), or pioglitazone (Pio group, n=69). The primary outcome was the difference in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels between the three groups at baseline to 24 weeks. For durability, the achievement of HbA1c levels <7% and <6.5% was compared in each group. The number of adverse events was investigated for safety.
Results
After 24 weeks of treatment, the change of HbA1c in the Alo+Pio, Alo, and Pio groups were –1.38%±0.08%, –1.03%±0.08%, and –0.84%±0.08%, respectively. The Alo+Pio group had significantly lower HbA1c levels than the other groups (P=0.0063, P<0.0001) and had a higher proportion of patients with target HbA1c achievement. In addition, insulin sensitivity and β-cell function, lipid profiles, and other metabolic indicators were also improved. There were no significant safety issues in patients treated with triple combination therapy.
Conclusion
Early combination triple therapy showed better efficacy and durability than the single add-on (dual) therapy. Therefore, combination therapy with metformin, alogliptin, and pioglitazone is a valuable early treatment option for T2DM poorly controlled with metformin monotherapy.
- Drug/Regimen
- Pioglitazone as Add-on THERAPY in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled with Dapagliflozin and Metformin: Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- Ji Hye Heo, Kyung Ah Han, Jun Hwa Hong, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jae Myung Yu, Hye Seung Jung, Bong-Soo Cha
- Received September 1, 2023 Accepted October 25, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0314 [Epub ahead of print]
- 1,203 View
- 114 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
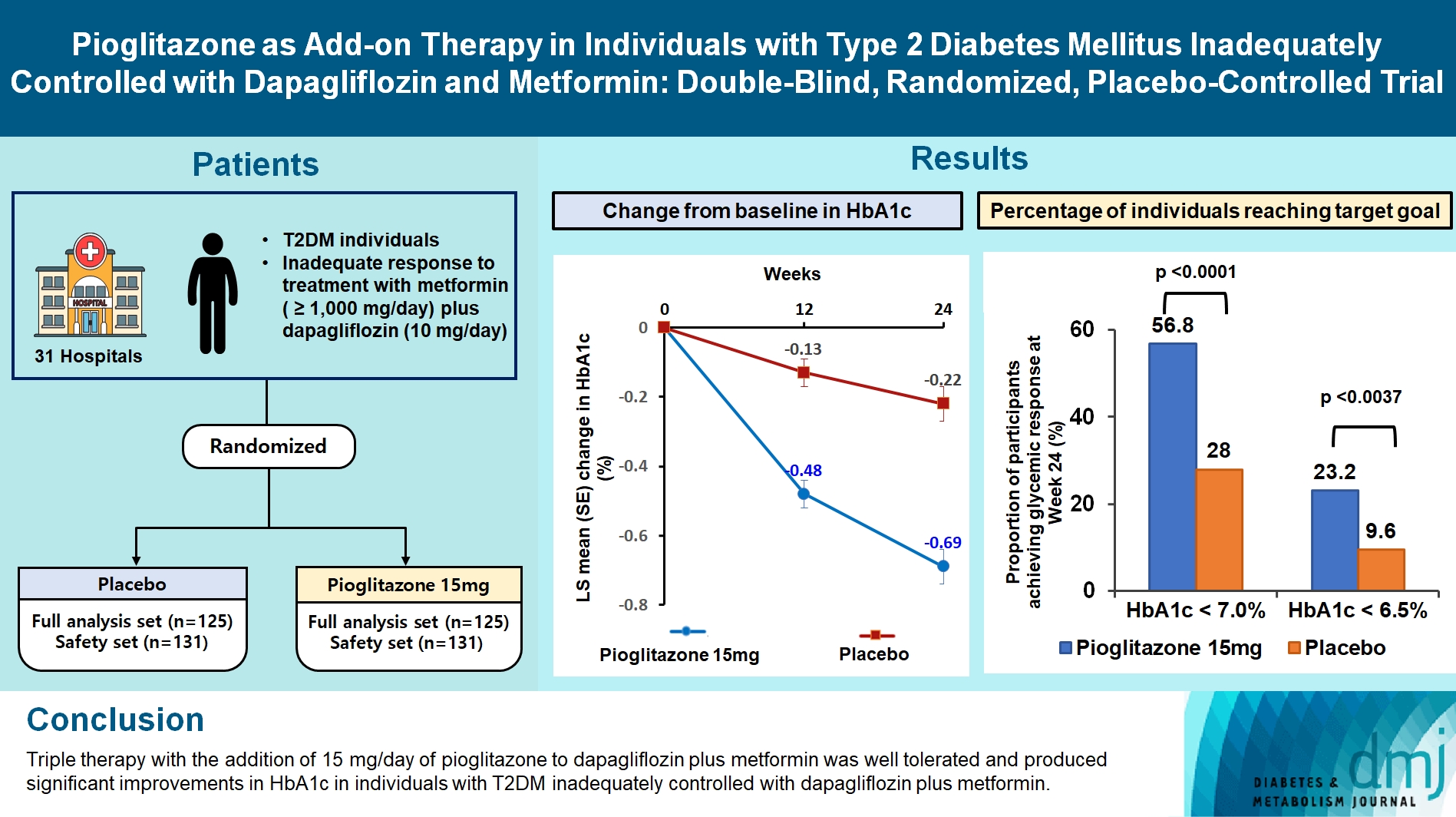
This study assessed the efficacy and safety of triple therapy with pioglitazone 15 mg add-on versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) inadequately controlled with metformin and dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, patients with T2DM with an inadequate response to treatment with metformin (≥1,000 mg/day) plus dapagliflozin (10 mg/day) were randomized to receive additional pioglitazone 15 mg/day (n=125) or placebo (n=125) for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels from baseline to week 24 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05101135).
Results
At week 24, the adjusted mean change from baseline in HbA1c level compared with placebo was significantly greater with pioglitazone treatment (–0.47%; 95% confidence interval, –0.61 to –0.33; P<0.0001). A greater proportion of patients achieved HbA1c <7% or <6.5% at week 24 with pioglitazone compared to placebo as add-on to 10 mg dapagliflozin and metformin (56.8% vs. 28% for HbA1c <7%, and 23.2% vs. 9.6% for HbA1c <6.5%; P<0.0001 for all). The addition of pioglitazone also significantly improved triglyceride, highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol levels, and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance levels, while placebo did not. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was similar between the groups, and the incidence of fluid retention-related side effects by pioglitazone was low (1.5%).
Conclusion
Triple therapy with the addition of 15 mg/day of pioglitazone to dapagliflozin plus metformin was well tolerated and produced significant improvements in HbA1c in patients with T2DM inadequately controlled with dapagliflozin plus metformin.
- Drug Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extension
- Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):808-817. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0387

- 2,575 View
- 281 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigates the long-term efficacy and safety of evogliptin add-on therapy in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) previously received dapagliflozin and metformin (DAPA/MET) combination.
Methods
In this multicenter randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, patients with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels 7.0% to 10.5% (n=283) previously used DAPA 10 mg plus MET (≥1,000 mg) were randomly assigned to the evogliptin 5 mg once daily or placebo group (1:1). The primary endpoint was the difference in the HbA1c level from baseline at week 24, and exploratory endpoints included the efficacy and safety of evogliptin over 52 weeks (trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04170998).
Results
Evogliptin add-on to DAPA/MET therapy was superior in HbA1c reduction compared to placebo at weeks 24 and 52 (least square [LS] mean difference, –0.65% and –0.55%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.79 to –0.51 and –0.71 to –0.39; P<0.0001). The proportion of patients achieving HbA1c <7% was higher in the triple combination group at week 52 (32.14% vs. 8.51% in placebo; odds ratio, 5.62; P<0.0001). Evogliptin significantly reduced the fasting glucose levels and mean daily glucose levels with improvement in homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function (LS mean difference, 9.04; 95% CI, 1.86 to 16.21; P=0.0138). Adverse events were similar between the groups, and no serious adverse drug reactions were reported in the evogliptin group.
Conclusion
Long-term triple combination with evogliptin added to DAPA/MET showed superior HbA1c reduction and glycemic control compared to placebo at 52 weeks and was well tolerated.
- Drug Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Enavogliflozin versus Dapagliflozin as Add-on to Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial
- Kyung Ah Han, Yong Hyun Kim, Doo Man Kim, Byung Wan Lee, Suk Chon, Tae Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, Jae Jin Nah, Hwa Rang Song, Seong In Cho, Seung-Ah Cho, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):796-807. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0315
- 40,042 View
- 572 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
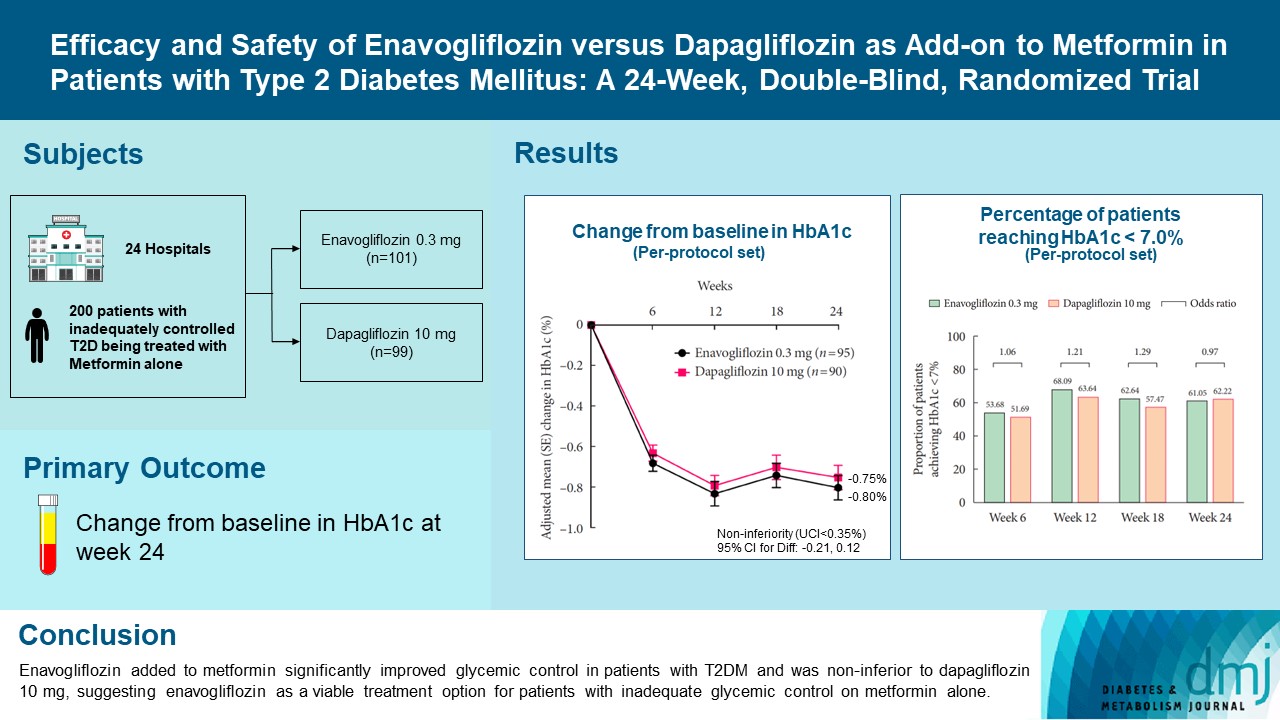
Enavogliflozin is a novel sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor currently under clinical development. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin as an add-on to metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) against dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, 200 patients were randomized to receive enavogliflozin 0.3 mg/day (n=101) or dapagliflozin 10 mg/day (n=99) in addition to ongoing metformin therapy for 24 weeks. The primary objective of the study was to prove the non-inferiority of enavogliflozin to dapagliflozin in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) change at week 24 (non-inferiority margin of 0.35%) (Clinical trial registration number: NCT04634500).
Results
Adjusted mean change of HbA1c at week 24 was –0.80% with enavogliflozin and –0.75% with dapagliflozin (difference, –0.04%; 95% confidence interval, –0.21% to 0.12%). Percentages of patients achieving HbA1c <7.0% were 61% and 62%, respectively. Adjusted mean change of fasting plasma glucose at week 24 was –32.53 and –29.14 mg/dL. An increase in urine glucose-creatinine ratio (60.48 vs. 44.94, P<0.0001) and decrease in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (–1.85 vs. –1.31, P=0.0041) were significantly greater with enavogliflozin than dapagliflozin at week 24. Beneficial effects of enavogliflozin on body weight (–3.77 kg vs. –3.58 kg) and blood pressure (systolic/diastolic, –5.93/–5.41 mm Hg vs. –6.57/–4.26 mm Hg) were comparable with those of dapagliflozin, and both drugs were safe and well-tolerated.
Conclusion
Enavogliflozin added to metformin significantly improved glycemic control in patients with T2DM and was non-inferior to dapagliflozin 10 mg, suggesting enavogliflozin as a viable treatment option for patients with inadequate glycemic control on metformin alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A 52‐week efficacy and safety study of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin as an add‐on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ENHANCE‐M extension study
Tae Seo Sohn, Kyung‐Ah Han, Yonghyun Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Suk Chon, In‐Kyung Jeong, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, JaeJin Na, Jae Min Cho, Seong In Cho, Wan Huh, Kun‐Ho Yoon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enavogliflozin, a potent and selective sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes
Sae Im Jeong, Mu Seong Ban, Jun‐Gi Hwang, Min‐Kyu Park, Soo Lim, Sejoong Kim, Soon Kil Kwon, Yoonjin Kim, Jae Min Cho, Jae Jin Na, Wan Huh, Jae‐Yong Chung
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of novel sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor enavogliflozin in type-2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, B.G. Harish, Beatrice Anne, Lakshmi Nagendra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102816. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Latest Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes
Nuri Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 148. CrossRef - Prospects of using sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)
Iryna Kostitska, Nadia Protas, Liliia Petrovska
Diabetes Obesity Metabolic Syndrome.2023; (5): 8. CrossRef - Navigating the Future of Diabetes Treatment with New Drugs: Focusing on the Possibilities and Prospects of Enavogliflozin
Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 769. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
- Lifestyle
- Body Fat Is Related to Sedentary Behavior and Light Physical Activity but Not to Moderate-Vigorous Physical Activity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Keun Hee An, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Seo Sohn, Ie Byung Park, Hae Jin Kim, Sung Dae Moon, Kyung Wan Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):316-325. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0029
- 5,475 View
- 138 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sedentary behavior (SB) has emerged as a new risk factor for cardiovascular accidents. We investigated whether physical activity levels or SB were related to percent body fat (%BF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods In this cross sectional study, we measured the duration of SB, light physical activity (LPA), moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), total energy expenditure, and step counts using a wireless activity tracker (Fitbit HR; FB) for 7 days in free-living conditions, along with %BF using a bio impedance analyzer (Inbody; Biospace) in 120 smartphone users with T2DM. Subjects were divided into exercise (Exe,
n =68) and non-exercise (nonExe,n =52) groups based on self-reports of whether the recommended exercises (30 min/day, 3 days/week for 3 months) were performed. SBt, LPAt, MVPAt were transformed from SB, LPA, MVPA for normally distributed variables.Results Participants were: female, 59.2%; age, 59.3±8.4 years; body mass index, 25.5±3.4 kg/m2; glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), 7.6%±1.2%; %BF, 30.4%±7.1%. They performed SB for 15.7±3.7 hr/day, LPA for 4.4±1.7 hr/day, and MVPA for 0.9±0.8 hr/day. The %BF was related to SBt and LPAt, but not to MVPA after adjustments for age, gender, and HbA1c. VPA was significantly higher in the Exe group than in the nonExe group, but SB, LPA, and moderate physical activity were not different. Predicted %BF was 89.494 to 0.105 (age), −13.047 (gender), −0.507 (HbA1c), −7.655 (LPAt) (F[4, 64]=62.929,
P <0.001), with anR 2 of 0.785 in multiple linear regression analysis.Conclusion Reduced body fat in elderly diabetic patients might be associated with reduced inactivity and increased LPA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Lotte Bogaert, Iris Willems, Patrick Calders, Eveline Dirinck, Manon Kinaupenne, Marga Decraene, Bruno Lapauw, Boyd Strumane, Margot Van Daele, Vera Verbestel, Marieke De Craemer
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(4): 102995. CrossRef - Association between depression, anemia and physical activity using isotemporal substitution analysis
Hee-kyoung Nam, Jungmi Park, Sung-il Cho
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Wearable Technologies in Health Research: Scoping Review
Sophie Huhn, Miriam Axt, Hanns-Christian Gunga, Martina Anna Maggioni, Stephen Munga, David Obor, Ali Sié, Valentin Boudo, Aditi Bunker, Rainer Sauerborn, Till Bärnighausen, Sandra Barteit
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2022; 10(1): e34384. CrossRef - The Correlation of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes With Adiposity in Adults
Juan Sun, Zhen Liu, Zimu Zhang, Ziyang Zeng, Weiming Kang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Physical Activity Assessment of Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Using Accelerometer-Based Cut Points: Scoping Review
Ioana A Moldovan, Alexa Bragg, Anna S Nidhiry, Barbara A De La Cruz, Suzanne E Mitchell
Interactive Journal of Medical Research.2022; 11(2): e34433. CrossRef - Effects of 4 Weeks of a Technique-Specific Protocol with High-Intensity Intervals on General and Specific Physical Fitness in Taekwondo Athletes: An Inter-Individual Analysis
Alex Ojeda-Aravena, Tomás Herrera-Valenzuela, Pablo Valdés-Badilla, Jorge Cancino-López, José Zapata-Bastias, José Manuel García-García
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3643. CrossRef - Inter-Individual Variability of a High-Intensity Interval Training With Specific Techniques vs. Repeated Sprints Program in Sport-Related Fitness of Taekwondo Athletes
Alex Ojeda-Aravena, Tomás Herrera-Valenzuela, Pablo Valdés-Badilla, Jorge Cancino-López, José Zapata-Bastias, José Manuel García-García
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - EFFECT OF SPORTS MEDICINE ON REDUCING BODY FAT PERCENTAGE AND LEAN BODY MASS
Chunyan Fan
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2021; 27(7): 714. CrossRef - Validation of the effectiveness of a digital integrated healthcare platform utilizing an AI-based dietary management solution and a real-time continuous glucose monitoring system for diabetes management: a randomized controlled trial
Sung Woon Park, Gyuri Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Woo Je Lee, Hyunjin Park, Jae Hyeon Kim
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Brain activity during a working memory task in different postures: an EEG study
Ju-Yeon Jung, Hwi-Young Cho, Chang-Ki Kang
Ergonomics.2020; 63(11): 1359. CrossRef
- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
- Arterial Stiffness by Aerobic Exercise Is Related with Aerobic Capacity, Physical Activity Energy Expenditure and Total Fat but not with Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Female Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Ji Yeon Jung, Kyung Wan Min, Hee Jung Ahn, Hwi Ryun Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Kang Seo Park, Kyung Ah Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(6):439-448. Published online December 15, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.6.439
- 4,664 View
- 32 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Arterial stiffness is an important factor in atherosclerosis. Thus we examined whether aerobic exercise could reduce arterial stiffness in obese women with type 2 diabetes without diabetic complication.
Methods A total of 35 women with type 2 diabetes (body mass index, 26.6±2.8 kg/m2; age, 56.4±1.9 years; duration of diabetes, 4.7±4.8 years) were assigned to aerobic exercise group (AEG) or control group (CG). AEG completed a 12-week exercise program (3.6 to 5.2 metabolic equivalents, 3 day/week, 60 min/day), with their exercise activities monitored by accelerometers. We measured abdominal total fat area (TFA), visceral fat area (VFA), and subcutaneous fat area (SFA) by computed tomography, insulin sensitivity by insulin tolerance test (KITT), and augmentation index (AIx) by SphygmoCor at baseline and at the end of the 12-week program.
Results The AIx was improved in the AEG compared with the CG (
P <0.001). The percent change of AIx had significant correlation with the improvement of physical activity energy expenditure (PAEE), aerobic capacity, TFA, and SFA (r =-0.416,P =0.013;r =0.560,P <0.001;r =0.489,P =0.003;r =0.531,P =0.001, respectively), but not with insulin sensitivity, energy intake, or VFA.Conclusion Improvement in aortic stiffness by aerobic exercise is related with the improvement of aerobic capacity, PAEE, and total fat but not with insulin sensitivity or energy intake in obese women with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between objectively measured physical activity and subclinical cardiovascular disease: a systematic review
Aparna Narendrula, Ellen Brinza, Christine Horvat Davey, Chris T Longenecker, Allison R Webel
BMJ Open Sport & Exercise Medicine.2024; 10(1): e001596. CrossRef - Aerobic training reduces pancreatic fat content and improves β‐cell function: A randomized controlled trial using IDEAL‐IQ magnetic resonance imaging
Min Li, Qidong Zheng, Joshua D. Miller, Panpan Zuo, Xiaodan Yuan, Jitao Feng, Chao Liu, Shan Bao, Qingqing Lou
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of aerobic exercise on waist circumference in adults with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Alex Armstrong, Klaus Jungbluth Rodriguez, Angelo Sabag, Yorgi Mavros, Helen M. Parker, Shelley E. Keating, Nathan A. Johnson
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Aortic waveform responses to insulin in late versus early chronotype with metabolic syndrome
Mary‐Margaret E. Remchak, Emily M. Heiston, Anna Ballantyne, Brielle L. Dotson, Steven K. Malin
Physiological Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise and ectopic fat in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
A. Sabag, K.L. Way, S.E. Keating, R.N. Sultana, H.T. O’Connor, M.K. Baker, V.H. Chuter, J. George, N.A. Johnson
Diabetes & Metabolism.2017; 43(3): 195. CrossRef - Arterial Stiffness Measured with the Cuff Oscillometric Method Is Predictive of Exercise Capacity in Patients with Cardiac Diseases
Yasushi Tazawa, Nobuyoshi Mori, Yoshiko Ogawa, Osamu Ito, Masahiro Kohzuki
The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine.2016; 239(2): 127. CrossRef
- Relationship between objectively measured physical activity and subclinical cardiovascular disease: a systematic review
- Effects of Aerobic Exercise Intensity on Abdominal and Thigh Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Attenuation in Overweight Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Yeon Jung, Kyung Ah Han, Hee Jung Ahn, Hwi Ryun Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Kang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(3):211-221. Published online June 14, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.3.211
- 4,453 View
- 40 Download
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the effects of exercise intensity on abdominal and mid-thigh adipose tissue, attenuation of skeletal muscle, and insulin sensitivity in overweight women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods Twenty-eight patients were randomly assigned to control (CG,
n =12), moderate intensity exercise (MEG,n =8), or vigorous intensity exercise (VEG,n =8) group. Subjects in both exercise groups completed a 12-week exercise program (MEG, 3.6 to 5.2 METs; VEG, ≥5.2 METs) that was monitored by accelerometers. We assessed body mass index (BMI), total fat area (TFA), visceral fat area (VFA), subcutaneous fat area (SFA), mid-thigh intramuscular adipose tissue (TIMAT), total skeletal muscle (TTM), low density skeletal muscle (TLDM), and normal density skeletal muscle (TNDM) using computed tomography, and measured insulin sensitivity with an insulin tolerance test (KITT), before and after the intervention.Results At baseline, the mean age was 53.8±7.9 years, duration of diabetes was 3.8±2.3 years, and BMI was 26.6±2.6 kg/m2. After 12 weeks, the percent change (%C) in BMI, TIMAT, and TLDM were not different among three groups. However, %C in TFA and VFA were significantly reduced in MEG compared to CG (
P =0.026 andP =0.008, respectively). %C SFA was significantly reduced in VEG compared to CG (P =0.038) and %C TTM, TNDM, and KITT were significantly increased in VEG compared to the CG (P =0.044,P =0.007, andP =0.016, respectively).Conclusion Although there was no difference in the change in BMI among groups, TFA and VFA were more reduced in MEG, and only VEG increased TTM, TNDM, and insulin sensitivity compared to CG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermuscular adipose tissue in metabolic disease
Bret H. Goodpaster, Bryan C. Bergman, Andrea M. Brennan, Lauren M. Sparks
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2023; 19(5): 285. CrossRef - Dose–response effects of exercise and caloric restriction on visceral adiposity in overweight and obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Francesco Recchia, Chit K. Leung, Angus P. Yu, Welton Leung, Danny J. Yu, Daniel Y. Fong, David Montero, Chi-Ho Lee, Stephen H.S. Wong, Parco M. Siu
British Journal of Sports Medicine.2023; 57(16): 1035. CrossRef - Muscle quality: the assessment, prognosis, and intervention
翔 畑中, 洋祐 大須賀
Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. Japanese Journal of Geriatrics.2023; 60(2): 103. CrossRef - Associations of Muscle Density and Area With Coronary Artery Plaque and Physical Function
Kristine M. Erlandson, Triin Umbleja, Michael T. Lu, Jana Taron, Heather J. Ribaudo, Edgar T. Overton, Rachel M. Presti, David W. Haas, Paul E. Sax, Michael T. Yin, Bingxue Kris Zhai, Rochelle Louis, Namrata Upadhyay, Parastou Eslami, Pamela S. Douglas, M
JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes.2023; 94(2): 174. CrossRef - Aerobic training reduces pancreatic fat content and improves β‐cell function: A randomized controlled trial using IDEAL‐IQ magnetic resonance imaging
Min Li, Qidong Zheng, Joshua D. Miller, Panpan Zuo, Xiaodan Yuan, Jitao Feng, Chao Liu, Shan Bao, Qingqing Lou
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of aerobic exercise on waist circumference in adults with overweight or obesity: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Alex Armstrong, Klaus Jungbluth Rodriguez, Angelo Sabag, Yorgi Mavros, Helen M. Parker, Shelley E. Keating, Nathan A. Johnson
Obesity Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of exercise on myosteatosis in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Yasmin Ezzatvar, Mikel Izquierdo, Antonio García-Hermoso
Journal of Applied Physiology.2021; 130(1): 245. CrossRef - Effect of exercise intervention dosage on reducing visceral adipose tissue: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yu-Hsuan Chang, Hui-Ying Yang, Shiow-Ching Shun
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(5): 982. CrossRef - Exercise Training to Decrease Ectopic Intermuscular Adipose Tissue in Individuals With Chronic Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Mauro Tuñón-Suárez, Alvaro Reyes-Ponce, Rodrigo Godoy-Órdenes, Nicolás Quezada, Marcelo Flores-Opazo
Physical Therapy.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Low-attenuation muscle is a predictor of diabetes mellitus: A population-based cohort study
Muhei Tanaka, Hiroshi Okada, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Muneaki Kumagai, Hiromi Nishimura, Michiaki Fukui
Nutrition.2020; 74: 110752. CrossRef - Drop-out ratio between moderate to high-intensity physical exercise treatment by patients with, or at risk of, type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Guillem Jabardo-Camprubí, Rafel Donat-Roca, Mercè Sitjà-Rabert, Raimon Milà-Villarroel, Judit Bort-Roig
Physiology & Behavior.2020; 215: 112786. CrossRef - High-Intensity Interval Training Versus Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training in Middle-Aged and Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial of the Acute Effects of Treadmill Walking on Glycemic Control
Romeu Mendes, Nelson Sousa, José Luís Themudo-Barata, Victor Machado Reis
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(21): 4163. CrossRef - Trunk muscle quality assessed by computed tomography: Association with adiposity indices and glucose tolerance in men
Alexandre Maltais, Natalie Alméras, Isabelle Lemieux, Angelo Tremblay, Jean Bergeron, Paul Poirier, Jean-Pierre Després
Metabolism.2018; 85: 205. CrossRef - Counting Footsteps with a Pedometer to Improve HMW Adiponectin and Metabolic Syndrome among Young Female Adults in the United Arab Emirates
Hayder Hasan, Amita Attlee, Hamid Jan Bin Jan Mohamed, Norliyana Aris, Wan Abdul Manan Bin Wan Muda
Journal of Obesity.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Exercise and ectopic fat in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
A. Sabag, K.L. Way, S.E. Keating, R.N. Sultana, H.T. O’Connor, M.K. Baker, V.H. Chuter, J. George, N.A. Johnson
Diabetes & Metabolism.2017; 43(3): 195. CrossRef - Effect of aerobic exercise intensity on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of head-to-head randomized trials
Yilina Liubaoerjijin, Tasuku Terada, Kevin Fletcher, Normand G. Boulé
Acta Diabetologica.2016; 53(5): 769. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta‐analysis on the effects of exercise training versus hypocaloric diet: distinct effects on body weight and visceral adipose tissue
R. J. H. M. Verheggen, M. F. H. Maessen, D. J. Green, A. R. M. M. Hermus, M. T. E. Hopman, D. H. T. Thijssen
Obesity Reviews.2016; 17(8): 664. CrossRef - Muscle wasting and aging: Experimental models, fatty infiltrations, and prevention
Thomas Brioche, Allan F. Pagano, Guillaume Py, Angèle Chopard
Molecular Aspects of Medicine.2016; 50: 56. CrossRef - Arterial Stiffness by Aerobic Exercise Is Related with Aerobic Capacity, Physical Activity Energy Expenditure and Total Fat but not with Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Female Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Ji Yeon Jung, Kyung Wan Min, Hee Jung Ahn, Hwi Ryun Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Kang Seo Park, Kyung Ah Han
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(6): 439. CrossRef - Intermuscular Fat: A Review of the Consequences and Causes
Odessa Addison, Robin L. Marcus, Paul C. LaStayo, Alice S. Ryan
International Journal of Endocrinology.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Relative Skeletal Muscle Mass Is Associated with Development of Metabolic Syndrome
Byung Sam Park, Ji Sung Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(6): 458. CrossRef
- Intermuscular adipose tissue in metabolic disease
- Cardiovascular Risk Assessment with Vascular Function, Carotid Atherosclerosis and the UKPDS Risk Engine in Korean Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
- Choon Sik Seon, Kyung Wan Min, Seung Yup Lee, Kyoung Woo Nho, Se Hwan Park, Bo Kyung Koo, Kyung Ah Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(6):619-627. Published online December 26, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.619
- 3,806 View
- 29 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Patients with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Few studies have evaluated the cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk simultaneously using the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) risk engine and non-invasive vascular tests in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
Methods Participants (
n =380; aged 20 to 81 years) with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes were free of clinical evidence of CVD. The 10-year coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke risks were calculated for each patient using the UKPDS risk engine. Carotid intima media thickness (CIMT), flow mediated dilation (FMD), pulse wave velocity (PWV) and augmentation index (AI) were measured. The correlations between the UKPDS risk engine and the non-invasive vascular tests were assessed using partial correlation analysis, after adjusting for age, and multiple regression analysis.Results The mean 10-year CHD and 10-year stroke risks were 14.92±11.53% and 4.03±3.95%, respectively. The 10-year CHD risk correlated with CIMT (
P <0.001), FMD (P =0.017), and PWV (P =0.35) after adjusting for age. The 10-year stroke risk correlated only with the mean CIMT (P <0.001) after adjusting for age. FMD correlated with age (P <0.01) and systolic blood pressure (P =0.09). CIMT correlated with age (P <0.01), HbA1c (P =0.05), and gender (P <0.01).Conclusion The CVD risk is increased at the onset of type 2 diabetes. CIMT, FMD, and PWV along with the UKPDS risk engine should be considered to evaluate cardiovascular disease risk in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of cardiovascular risk estimate with degree of atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mashkura Riyazuddeen, AliHasan Faiz Karnam, L Gopinath, Nayyar Iqbal
Journal of Current Research in Scientific Medicine.2019; 5(2): 94. CrossRef - Carotid atherosclerosis and its relationship to coronary heart disease and stroke risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yan Wu, Jie He, Xue Sun, Yi-Ming Zhao, Han-Yu Lou, Xiao-li Ji, Xiao-Hong Pang, Li-Zhen Shan, Ying-Xiu Kang, Jun Xu, Song-Zhao Zhang, Yong-Jian Wang, Yue-Zhong Ren, Peng-Fei Shan
Medicine.2017; 96(39): e8151. CrossRef - Diabetes Associated to Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Patients of Family Health Unity
Polyane Medeiros Alves, Raiane dos Santos Pereira, Ariel Gustavo Letti, Álvaro Luís Müller da Fonseca
Open Journal of Preventive Medicine.2015; 05(04): 177. CrossRef - Independent Association of Circulating Level of Chemerin With Functional and Early Morphological Vascular Changes in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Bin Lu, Ming Zhao, Weimin Jiang, Jian Ma, Cuihua Yang, Jiaqing Shao, Ping Gu
Medicine.2015; 94(47): e1990. CrossRef - Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Chun-Ja Kim, Hee Sun Kang, Elizabeth A. Schlenk, Sun-Mi Chae
The Diabetes Educator.2015; 41(2): 203. CrossRef - Urinary adiponectin concentration is positively associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications
Won Seon Jeon, Ji Woo Park, Namseok Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Won Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Cheol-Young Park, Byung-Soo Youn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and a Pilot Test of an Internet-Based Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Program for Korean Male Workers With Metabolic Syndrome
CHUN-JA KIM, SEWON KANG
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2013; 31(4): 157. CrossRef - Risk Factors for the Progression of Intima-Media Thickness of Carotid Arteries: A 2-Year Follow-Up Study in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
Sang Ouk Chin, Jin Kyung Hwang, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, You-Cheol Hwang, Seungjoon Oh, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Jeong-taek Woo, Sung-Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim, Ja-Heon Kang, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(5): 365. CrossRef - Epicardial adipose tissue thickness is an indicator for coronary artery stenosis in asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients: its assessment by cardiac magnetic resonance
Hyun Kim, Kwang Kim, Hye-Jeong Lee, Hee Yu, Jae Moon, Eun Kang, Bong Cha, Hyun Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Young Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012; 11(1): 83. CrossRef - Potential association between coronary artery disease and the inflammatory biomarker YKL-40 in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hyun Min Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Young-Mi Song, Won Jin Kim, Hyuk-Jae Chang, Dong-Hoon Choi, Hee Tae Yu, EunSeok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of cardiovascular risk estimate with degree of atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Response: The Effect of an Angiotensin Receptor Blocker on Arterial Stiffness in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Hypertension (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:236-42)
- Ji Hyun Kim, Su Jin Oh, Jung Min Lee, Eun Gyoung Hong, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Ah Han, Kyung Wan Min, Hyun Shik Son, Sang Ah Chang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):429-430. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.429
- 3,747 View
- 27 Download
- The Correlations between Extremity Circumferences with Total and Regional Amounts of Skeletal Muscle and Muscle Strength in Obese Women with Type 2 Diabetes
- Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Hee Jung Ahn, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):374-383. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.374
- 4,286 View
- 43 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Insulin resistance is related to central obesity and the amount of skeletal muscle. A simple and practical anthropometric marker for muscle mass is not known, although waist circumference (WC) is used as an indicator of abdominal obesity. The aims of this study were to investigate whether arm (AC) and thigh circumferences (TC) can be used as an indicator of muscle mass and if they are related to muscle strength.
Methods A total of 110 obese (body mass index [BMI]≥25 kg/m2) women with type 2 diabetes were enrolled, and WC, AC, and TC were measured. Abdominal visceral fat (AVF), subcutaneous fat (ASF), and total fat (ATF) were assessed by computed tomography, regional muscle (MM), and fat mass by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, muscle strength by one repetition maximum (1RM) of both extremities (chest and leg press) and insulin resistance by KITT.
Results The mean age was 56.2±7.3 years, duration of diabetes was 4.2±4.4 years, and BMI was 27.2±2.8 kg/m2. WC was correlated with ATF, AVF, and ASF (
r =0.728,P <0.001;r =0.515,P <0.001;r =0.608,P <0.001, respectively). Arm MM was correlated with AC (r =0.500,P <0.001), and leg MM with TC (r =0.291,P =0.002). Upper 1RM was related to AC/WC ratio (r =0.359,P <0.001), and lower 1RM was to TC/WC ratio (r =0.286,P =0.003). Insulin resistance had significant relations with AVF, WC, and total MM (r =-0.262,P =0.008;r =-0.217,P =0.029;r =0.160,P =0.031, respectively).Conclusion The muscle mass was related to extremity circumferences, and muscle strength was to extremity/waist circumference ratio in obese women with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inflammation and Loss of Skeletal Muscle Mass in Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
Joana Ferreira, Alexandre Carneiro, Isabel Vila, Cristina Silva, Cristina Cunha, Adhemar Longatto-Filho, Amílcar Mesquita, Jorge Cotter, Armando Mansilha, Margarida Correia-Neves, Pedro Cunha
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2023; 88: 164. CrossRef - Thigh-hip ratio is significantly associated with all-cause mortality among Japanese community-dwelling men
Ryuichi Kawamoto, Asuka Kikuchi, Daisuke Ninomiya, Teru Kumagi, Fredirick Lazaro mashili
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(10): e0292287. CrossRef - Association of Skeletal Muscle and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
Joana Ferreira, Alexandre Lima Carneiro, Isabel Vila, Cristina Cunha, C ristina Silva, Adhemar Longatto-Filho, Amesqui Mesquita, Jorge Cotter, Armando Mansilha, Margarida Correia-Neves, Pedro Cunha
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2022; 80: 223. CrossRef - A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the hypoglycemic efficacy of the mcIRBP-19-containing Momordica charantia L. fruit extracts in the type 2 diabetic subjects
Yi-Sun Yang, Nian-Yi Wu, Edy Kornelius, Chien-Ning Huang, Nae-Cherng Yang
Food & Nutrition Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Thigh circumference and handgrip strength are significantly associated with all-cause mortality: findings from a study on Japanese community-dwelling persons
Ryuichi Kawamoto, Asuka Kikuchi, Taichi Akase, Daisuke Ninomiya, Teru Kumagi
European Geriatric Medicine.2021; 12(6): 1191. CrossRef Thigh Circumference and Risk of All-Cause, Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Mortality: A Cohort Study
Chao-lei Chen, Lin Liu, Jia-yi Huang, Yu-ling Yu, Geng Shen, Kenneth Lo, Yu-qing Huang, Ying-qing Feng
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2020; Volume 13: 1977. CrossRef- Mid-arm muscle circumference as an indicator of osteoporosis in community-dwelling older men
Yuan-Ping Chao, Tung-Wei Kao, Wei-Liang Chen, Tao-Chun Peng, Li-Wei Wu
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2020; 87: 103998. CrossRef - Carnitine deficiency is associated with decreased exercise activity in hemodialysis patients
Junko Yano, Yusuke Kaida, Yosuke Nakayama, Sakuya Ito, Yuka Kurokawa, Nao Nakamura, Takuma Hazama, Takashi Maeda, Ryuki Hashida, Kyoko Tashiro, Takahiro Inokuchi, Hiroo Matsuse, Kei Fukami
Renal Replacement Therapy.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Preliminary study of the anabolic/catabolic balance in patients with interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
Ahmed El Hosainy, Safy Kaddah, Mohamed Saied, Aml Ibrahim, Rania Darwish
Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis.2017; 66(3): 497. CrossRef - Anthropometric dimensions provide reliable estimates of abdominal adiposity: A validation study
Z. Pintér, A. Pósa, C. Varga, I. Horváth, A. Palkó, Z. Just, G. Pálfi
HOMO.2017; 68(5): 398. CrossRef - Creatine kinase in the U.S. population
Michael D. George, Neilia-Kay McGill, Joshua F. Baker
Medicine.2016; 95(33): e4344. CrossRef - Relationship of calf circumference with bone mineral density and hip geometry: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
Rekha Singh, Sushil Gupta
Archives of Osteoporosis.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Acupuncture for Management of Balance Impairment in a Patient with Bipolar Disorder
Kun Hyung Kim, Jae Kyu Kim, Gi Young Yang, Byung Ryul Lee, Seung Hee Noh
Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies.2013; 6(1): 56. CrossRef - The association of insulin resistance and carotid atherosclerosis with thigh and calf circumference in patients with type 2 diabetes
Jong Suk Park, Min Ho Cho, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim, Kap Bum Huh
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inflammation and Loss of Skeletal Muscle Mass in Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
- Effects of Aerobic Exercise vs. Resistance Training on Endothelial Function in Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Wan Min, Hee Jung Ahn, Hee Geum Seok, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gang Seo Park, Kyung Ah Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):364-373. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.364
- 6,453 View
- 96 Download
- 62 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background There is controversy over whether aerobic or resistance exercise is more effective for improving endothelial function in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study was aimed to investigate the effects of an aerobic and resistance training program on endothelial function, and the influences of glycemic control, body weight changes, and aerobic capacity in T2DM.
Methods Total 40 overweight women with T2DM were assigned into 3 groups: an aerobic exercise group (AEG,
n =13), resistance exercise group (REG,n =12), and control group (CG,n =15), and followed either brisk walking for the AEG or resistance band training for the REG, 60 minutes per day, 5 days per week for 12 weeks with monitoring daily activity using accelerometers. We assessed endothelial function by flow-mediated dilation (FMD), and aerobic capacity by oxygen uptake at anaerobic threshold (AT_VO2) at baseline and following training program.Results The mean participants' age was 57.0±6.8 years, and body mass index (BMI) was 27.0±2.3 kg/m2. After intervention, FMD increased by 2.2±1.9% in AEG, which differed from REG and CG (
P =0.002), despite of decreased body weight (BW) in both AG and RG (2.8±2.5%,P =0.002; 1.6±2.0%,P =0.017, respectively). A significant increased AT_VO2 and decreased HbA1c were found only in AEG. In all participants, FMD was changed with the significant relations to the AT_VO2 (r =0.348,P =0.035), but not to HbA1c levels or BW.Conclusion Aerobic exercise appears to be more beneficial than resistance exercise for improving endothelial function in T2DM. In addition, aerobic capacity could be a better predictor of changes in FMD than BW and glycemic control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of exercise on flow-mediated dilation in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Bopeng Qiu, Yilun Zhou, Xifeng Tao, Xiao Hou, Liwen Du, Yuanyuan Lv, Laikang Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Resistance Exercise Training on Glycemic Control Among Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Yuwen Wan, Zhanguo Su
Biological Research For Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low-Intensity Resistance Training Improves Flow-Mediated Dilation in Young Hispanic Adults
José M. Briceño-Torres, Elizabeth Carpio-Rivera, Andrea Solera-Herrera, Jeffrey Forsse, Peter W. Grandjean, José Moncada-Jiménez
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research.2023; 37(2): 298. CrossRef - Intensity Differences of Resistance Training for Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tenglong Fan, Man-Hsu Lin, Kijin Kim
Healthcare.2023; 11(3): 440. CrossRef - Effect of continuous aerobic exercise on endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Xifeng Tao, Yiyan Chen, Kai Zhen, Shiqi Ren, Yuanyuan Lv, Laikang Yu
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Original article – Effect of different resistance training intensities on endothelial function in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review
Thiago Borges Madureira Sabino, Denise Maria Martins Vancea, Manoel da Cunha Costa, Raphael José Perrier de Melo, Iago Vilela Dantas, Jonathan Nicolas dos Santos Ribeiro
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 200: 110676. CrossRef - 장기간의 저항성 트레이닝이 전문 보디빌더의 중심 동맥 혈압 및 경직도에 미치는 영향
동현 이, 원일 박, 재성 이, 형진 백, 광석 홍
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2023; 62(4): 1. CrossRef - Dose-response relationships of resistance training in Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wanying Su, Meiyi Tao, Lin Ma, Ke Tang, Fang Xiong, Xuan Dai, Yuelan Qin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight into type 2 diabetes impaired exercising mitochondrial oxidative flux: is it blood flow, mitochondria, or neither?
Noah A. John, Liam T. O'Brien
The Journal of Physiology.2022; 600(4): 707. CrossRef - Does exercise training improve the function of vascular smooth muscle? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yujia Liu, Zhenjia Sun, Tong Chen, Chen Yang
Research in Sports Medicine.2022; 30(6): 577. CrossRef - Effect of resistance training on HbA1c in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the moderating effect of changes in muscular strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Anna K Jansson, Li X Chan, David R Lubans, Mitch J Duncan, Ronald C Plotnikoff
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(2): e002595. CrossRef - Does Aerobic plus Machine-Assisted Resistance Training Improve Vascular Function in Type 2 Diabetes? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials with Trial Sequential Analysis
Xianshan Guo, Shizhe Guo, Hongmei Zhang, Zhen Li
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(15): 4257. CrossRef - Endurance Training Depletes Antioxidant System but Does Not Affect Endothelial Functions in Women with Abdominal Obesity: A Randomized Trial with a Comparison to Endurance-Strength Training
Małgorzata Jamka, Paweł Bogdański, Patrycja Krzyżanowska-Jankowska, Anna Miśkiewicz-Chotnicka, Joanna Karolkiewicz, Monika Duś-Żuchowska, Radosław Mądry, Aleksandra Lisowska, Anna Gotz-Więckowska, Saule Iskakova, Jarosław Walkowiak, Edyta Mądry
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(8): 1639. CrossRef - The Role of Physical Therapy in the Combined Treatment of Patients with Lower Extremities Diabetic Angiopathies
Denis V. Frolov
Bulletin of Rehabilitation Medicine.2021; 20(2): 80. CrossRef - Low-to-Moderate-Intensity Resistance Exercise Is More Effective than High-Intensity at Improving Endothelial Function in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yong Zhang, Ya-Jun Zhang, Hong-Wei Zhang, Wei-Bing Ye, Mallikarjuna Korivi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(13): 6723. CrossRef - Effects of resistance training on endothelial function: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jessika Karla T.N.F. Silva, Annelise L. Menêses, Belinda J. Parmenter, Raphael M. Ritti-Dias, Breno Q. Farah
Atherosclerosis.2021; 333: 91. CrossRef - Vascular Ageing and Aerobic Exercise
Michaela Kozakova, Carlo Palombo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(20): 10666. CrossRef - High-Intensity Endurance and Strength Training in Water Polo Olympic Team Players: Impact on Arterial Wall Properties
Evangelos Oikonomou, Gerasimos Siasos, Georgios Marinos, Marina Zaromitidou, Dimitris Athanasiou, Petros Fountoulakis, Sotiris Tsalamandris, Georgios Charalambous, Georgios Lazaros, Charalambos Vlachopoulos, Dimitris Tousoulis
Cardiology.2021; 146(1): 119. CrossRef - Beyond general resistance training. Hypertrophy versus muscular endurance training as therapeutic interventions in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Pedro Acosta‐Manzano, María Rodriguez‐Ayllon, Francisco M. Acosta, David Niederseer, Josef Niebauer
Obesity Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Aerobic Exercise Increases Tear Secretion and Decreases Inflammatory Cytokines in Healthy Subjects
Hao Li, Fei Li, Rouxi Zhou, Kai Gao, Lingyi Liang, Xiulan Zhang
Asia-Pacific Journal of Ophthalmology.2020; 9(5): 404. CrossRef - The Role of Aerobic Training Variables Progression on Glycemic Control of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: a Systematic Review with Meta-analysis
Rodrigo Sudatti Delevatti, Cláudia Gomes Bracht, Salime Donida Chedid Lisboa, Rochelle Rocha Costa, Elisa Corrêa Marson, Nathalie Netto, Luiz Fernando Martins Kruel
Sports Medicine - Open.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Exercise on Risk Factors of Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Fuyuan Liao, Ruopeng An, Fang Pu, Stephanie Burns, Sa Shen, Yih-Kuen Jan
American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation.2019; 98(2): 103. CrossRef - Therapeutic Options Targeting Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Inflammation to Hinder the Progression of Vascular Complications of Diabetes
João S. Teodoro, Sara Nunes, Anabela P. Rolo, Flávio Reis, Carlos M. Palmeira
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of short-term resistance training on endothelial function and inflammation markers in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial
Anderson Rech, Cíntia Ehlers Botton, Pedro Lopez, André Quincozes-Santos, Daniel Umpierre, Ronei Silveira Pinto
Experimental Gerontology.2019; 118: 19. CrossRef - Resistance Exercise Intensity is Correlated with Attenuation of HbA1c and Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yubo Liu, Weibing Ye, Qian Chen, Yong Zhang, Chia-Hua Kuo, Mallikarjuna Korivi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(1): 140. CrossRef - Effects of Resistance Exercise on Glycated Hemoglobin and Functional Performance in Older Patients with Comorbid Diabetes Mellitus and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Trial
Shu-Mei Chen, Feng-Chih Shen, Jung-Fu Chen, Wen-Dien Chang, Nai-Jen Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 17(1): 224. CrossRef - Endothelial function following interval exercise plus low‐calorie diet treatment in obese females
Nicole M. Gilbertson, Stephanie L. Miller, Natalie Z.M. Eichner, Steven K. Malin
Physiological Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of exercise on vascular endothelial function in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jung-Hoon Lee, Ruda Lee, Moon-Hyon Hwang, Marc T. Hamilton, Yoonjung Park
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise training and endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Han Yin, Zilin Sun, Martina Zügel, Jürgen Michael Steinacker, Uwe Schumann
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Responses of healthy young males to fine-particle exposure are modified by exercise habits: a panel study
Xi Chen, Wu Chen, Yanwen Wang, Yiqun Han, Tong Zhu
Environmental Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Aerobic exercise regulates blood lipid and insulin resistance via the toll‑like receptor 4‑mediated extracellular signal‑regulated kinases/AMP‑activated protein kinases signaling pathway
Mei Wang, Sen Li, Fubaihui Wang, Jinhui Zou, Yanfeng Zhang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Efectos del ejercicio físico en los factores de riesgo cardiovascular que constituyen el síndrome metabólico: una alternativa para reducir su tendencia
Adrián Hernández Alonso
Revista Colombiana de Médicina Física y Rehabilitación.2017; 27(2): 140. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory effects of active commuting and leisure time exercise in overweight and obese women and men: A randomized controlled trial
Anne Sofie Gram, Else-Marie Bladbjerg, Jonas Salling Quist, Martin Bæk Petersen, Mads Rosenkilde, Bente Stallknecht
Atherosclerosis.2017; 265: 318. CrossRef - The Effects of Exercise Training on Brachial Artery Flow-Mediated Dilation
Kate S. Early, Abigail Stewart, Neil Johannsen, Carl J. Lavie, Jerry R. Thomas, Michael Welsch
Journal of Cardiopulmonary Rehabilitation and Prevention.2017; 37(2): 77. CrossRef - Effects of Self-directed Exercise Programmes on Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review Evaluating Their Effect on HbA1c and Other Metabolic Outcomes, Physical Characteristics, Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Functional Outcomes
Hugh Byrne, Brian Caulfield, Giuseppe De Vito
Sports Medicine.2017; 47(4): 717. CrossRef - Effects of Combination of Baduanjin and Elastic Band on Physical Fitness and Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
强 庄
Advances in Physical Sciences.2017; 05(01): 5. CrossRef - Effects of progressive resistance training and weight loss versus weight loss alone on inflammatory and endothelial biomarkers in older adults with type 2 diabetes
Eliza G. Miller, Parneet Sethi, Caryl A. Nowson, David W. Dunstan, Robin M. Daly
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2017; 117(8): 1669. CrossRef - Endurance exercise per se reduces the cardiovascular risk marker t-PA antigen in healthy, younger, overweight men
Else-Marie Bladbjerg, Jane Skov, Pernille Nordby, Bente Stallknecht
Thrombosis Research.2017; 152: 69. CrossRef - Effect of Exercise Intervention on Flow-Mediated Dilation in Overweight and Obese Adults: Meta-Analysis
Younsun Son, Kyungun Kim, Soeun Jeon, Minsoo Kang, Sukho Lee, Yoonjung Park
International Journal of Vascular Medicine.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Effects of Elastic Band Resistance Training on Glucose Control, Body Composition, and Physical Function in Women With Short- vs. Long-Duration Type-2 Diabetes
Bong-Sup Park, Andy V. Khamoui, Lee E. Brown, Do-Youn Kim, Kyung-Ah Han, Kyung-Wan Min, Geun-Hee An
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research.2016; 30(6): 1688. CrossRef - Glycemic reductions following water- and land-based exercise in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Rodrigo Sudatti Delevatti, Carolina Dertzbocher Feil Pinho, Ana Carolina Kanitz, Cristine Lima Alberton, Elisa Corrêa Marson, Luciana Peruchena Bregagnol, Salime Chedid Lisboa, Beatriz D. Schaan, Luiz Fernando Martins Kruel
Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice.2016; 24: 73. CrossRef - Short-term exercise training improves flow-mediated dilation and circulating angiogenic cell number in older sedentary adults
Rian Q. Landers-Ramos, Kelsey J. Corrigan, Lisa M. Guth, Christine N. Altom, Espen E. Spangenburg, Steven J. Prior, James M. Hagberg
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2016; 41(8): 832. CrossRef - Glucose control can be similarly improved after aquatic or dry-land aerobic training in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized clinical trial
Rodrigo S. Delevatti, Ana Carolina Kanitz, Cristine L. Alberton, Elisa Corrêa Marson, Salime Chedid Lisboa, Carolina Dertzbocher Feil Pinho, Gisele A. Lovatel, Arthiese Korb, Karine Bertoldi, Rodrigo C.O. Macedo, Ionara R. Siqueira, Beatriz D. Schaan, Lui
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.2016; 19(8): 688. CrossRef - Assessment of endothelial function by flow-mediated dilation in diabetic patients: Effects of physical exercise
Aline P Jarrete, Angelina Zanesco, Maria Andréia Delbin
Motriz: Revista de Educação Física.2016; 22(1): 3. CrossRef - Psychosocial Variables Related to Why Women are Less Active than Men and Related Health Implications
Elizabeth Skidmore Edwards, Sarah Carson Sackett
Clinical Medicine Insights: Women's Health.2016; 9s1: CMWH.S34668. CrossRef - In Search of the Ideal Resistance Training Program to Improve Glycemic Control and its Indication for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hajime Ishiguro, Satoru Kodama, Chika Horikawa, Kazuya Fujihara, Ayumi Sugawara Hirose, Reiko Hirasawa, Yoko Yachi, Nobumasa Ohara, Hitoshi Shimano, Osamu Hanyu, Hirohito Sone
Sports Medicine.2016; 46(1): 67. CrossRef - Effects of exercise training using resistance bands on glycaemic control and strength in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Samantha K. McGinley, Marni J. Armstrong, Normand G. Boulé, Ronald J. Sigal
Acta Diabetologica.2015; 52(2): 221. CrossRef - Impact of combined exercise training on cardiovascular autonomic control and mortality in diabetic ovariectomized rats
Iris C. Sanches, Filipe F. Conti, Nathalia Bernardes, Janaina de O Brito, Elia G. Galdini, Cláudia R. Cavaglieri, Maria-Cláudia Irigoyen, Kátia De Angelis
Journal of Applied Physiology.2015; 119(6): 656. CrossRef - Three months of strictly controlled daily endurance exercise reduces thrombin generation and fibrinolytic risk markers in younger moderately overweight men
Anne Sofie Gram, Else-Marie Bladbjerg, Jane Skov, Thorkil Ploug, Anders Sjödin, Mads Rosenkilde, Daniel Elenius Madsen, Bente Merete Stallknecht
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2015; 115(6): 1331. CrossRef - Exercise Modalities and Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review and Dose–Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Ammar W. Ashor, Jose Lara, Mario Siervo, Carlos Celis-Morales, Clio Oggioni, Djordje G. Jakovljevic, John C. Mathers
Sports Medicine.2015; 45(2): 279. CrossRef - The Impact of High-Intensity Interval Training Versus Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training on Vascular Function: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Joyce S. Ramos, Lance C. Dalleck, Arnt Erik Tjonna, Kassia S. Beetham, Jeff S. Coombes
Sports Medicine.2015; 45(5): 679. CrossRef - Safety of Aerobic Exercise in People With Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Single-Group Clinical Trial
Patricia M. Kluding, Mamatha Pasnoor, Rupali Singh, Linda J. D'Silva, Min Yoo, Sandra A. Billinger, Joseph W. LeMaster, Mazen M. Dimachkie, Laura Herbelin, Douglas E. Wright
Physical Therapy.2015; 95(2): 223. CrossRef - Sleep and exercise: A reciprocal issue?
Mounir Chennaoui, Pierrick J. Arnal, Fabien Sauvet, Damien Léger
Sleep Medicine Reviews.2015; 20: 59. CrossRef - Blood glucose response to aerobic exercise training program among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus at the University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu South-East, Nigeria
C. I. Ezema, S. Lamina, Amarachi A. Onwunali, U. A. Ezugwu, A. A. Amaeze, M. J. Nwankwo
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2015; 35(S2): 88. CrossRef - Endothelial Function Increases after a 16-Week Diet and Exercise Intervention in Overweight and Obese Young Women
Lisa M. Cotie, Andrea R. Josse, Stuart M. Phillips, Maureen J. MacDonald
BioMed Research International.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Impact of different training modalities on glycaemic control and blood lipids in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Lukas Schwingshackl, Benjamin Missbach, Sofia Dias, Jürgen König, Georg Hoffmann
Diabetologia.2014; 57(9): 1789. CrossRef - Exercise as a Therapeutic Strategy for Primary Mitochondrial Cytopathies
Mark A. Tarnopolsky
Journal of Child Neurology.2014; 29(9): 1225. CrossRef - Effects of weight management by exercise modes on markers of subclinical atherosclerosis and cardiometabolic profile among women with abdominal obesity: a randomized controlled trial
Jina Choo, Juneyoung Lee, Jeong-Hyun Cho, Lora E Burke, Akira Sekikawa, Sae Young Jae
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Walking disability in patients with peripheral artery disease is associated with arterial endothelial function
S. Marlene Grenon, Karen Chong, Hugh Alley, Emily Nosova, Warren Gasper, Jade Hiramoto, W. John Boscardin, Christopher D. Owens
Journal of Vascular Surgery.2014; 59(4): 1025. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Function and Predictors of Exercise Capacity in Patients With Colorectal Cancer
Larissa Cramer, Bert Hildebrandt, Thomas Kung, Kristin Wichmann, Jochen Springer, Wolfram Doehner, Anja Sandek, Miroslava Valentova, Tatjana Stojakovic, Hubert Scharnagl, Hanno Riess, Stefan D. Anker, Stephan von Haehling
Journal of the American College of Cardiology.2014; 64(13): 1310. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise Training on Arterial Function in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
David Montero, Guillaume Walther, Eric Benamo, Antonia Perez-Martin, Agnès Vinet
Sports Medicine.2013; 43(11): 1191. CrossRef - A randomized trial of exercise for blood pressure reduction in type 2 diabetes: Effect on flow-mediated dilation and circulating biomarkers of endothelial function
Bethany Barone Gibbs, Devon A. Dobrosielski, Susanne Bonekamp, Kerry J. Stewart, Jeanne M. Clark
Atherosclerosis.2012; 224(2): 446. CrossRef
- The effect of exercise on flow-mediated dilation in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Small Rice Bowl-Based Meal Plan for Energy and Marcronutrient Intake in Korean Men with Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study
- Hee Jung Ahn, Kyung Ah Han, Jin Young Jang, Jae Hyuk Lee, Kang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(3):273-281. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.273
- 65,535 View
- 37 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Koreans eat rice, which is usually served in a rice bowl. We investigated the effect of a meal plan using small rice bowls on the total energy intake (TEI) and the marcronutrient intake in Korean men with type 2 diabetes.
Methods A total of 62 men with type 2 diabetes were divided by body mass index (BMI) (normal weight [NW], BMI<23 kg/m2; overweight [OW], 23≤BMI<25 kg/m2; obese [OB], BMI≥25 kg/m2) and proportions of carbohydrate intake to TEI (PCI) (low carbohydrate intake [LC], <55%; recommended carbohydrate intake [RC], ≥55% and ≤60%; high carbohydrate intake [HC], >60%). The 3-day dietary records were analyzed for TEI and proportions of macronutrients, before and 2 weeks after a small-sized (300 mL) rice bowl based education was given.
Results There were no significant differences in the age and BMI within the sub-groups by BMI and PCI groups. In baseline, the ratio of TEI to recommended total energy intake (RTR) of OW and OB were higher than that of NW. The PCI of HC was higher than that of LC and alcohol intake of HC was lower than that of LC. After education, the reduction of RTREI in OB was higher than that in OW and NW. The reduction of PCI in HC was higher than that of LC.
Conclusion A small rice bowl based meal plan was effective for the reduction of energy intake and control of marcronutrient intake in Korean obese men with type 2 diabetes consuming a high carbohydrate diet.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - The association between measurement sites of visceral adipose tissue and cardiovascular risk factors after caloric restriction in obese Korean women
Hye-Ok Lee, Jung-Eun Yim, Jeong-Sook Lee, Young-Seol Kim, Ryowon Choue
Nutrition Research and Practice.2013; 7(1): 43. CrossRef - Daily Rice Intake Strongly Influences the Incidence of Metabolic Syndrome in Japanese Men Aged 40-59 Years
Yoko Watanabe, Isao Saito, Yasuhiko Asada, Taro Kishida, Tatsuhiro Matsuo, Masamitsu Yamaizumi, Tadahiro Kato
Journal of Rural Medicine.2013; 8(1): 161. CrossRef
- Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
- The Effect of an Angiotensin Receptor Blocker on Arterial Stiffness in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Hypertension
- Ji Hyun Kim, Su Jin Oh, Jung Min Lee, Eun Gyoung Hong, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Ah Han, Kyung Wan Min, Hyun Shik Son, Sang Ah Chang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(3):236-242. Published online June 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.236
- 28,950 View
- 35 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus are major risk factors for cardiovascular disease. This study analyzed the changes in central aortic waveforms and pulse wave velocity as well as related parameters after treatment with valsartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker, in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
Methods We used pulse wave analysis to measure central aortic waveform in a total of 98 subjects. In 47 of these patients, pulse wave velocity measurements were obtained before and after 12 weeks of treatment with valsartan.
Results In the central aortic waveform analysis, the aortic pulse pressure and augmentation index were significantly decreased after valsartan treatment, as was the aortic pulse wave velocity. Factors contributing to the improvement in pulse wave velocity were the fasting blood glucose and haemoglobin A1c levels.
Conclusion Short-term treatment with valsartan improves arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension, and the glucose status at baseline was associated with this effect.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mechanisms underlying the blood pressure‐lowering effects of empagliflozin, losartan and their combination in people with type 2 diabetes: A secondary analysis of a randomized crossover trial
Rosalie A. Scholtes, Charlotte M. Mosterd, Anne C. Hesp, Mark M. Smits, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, Daniël H. van Raalte
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(1): 198. CrossRef - Distinct effects of losartan and atenolol on vascular stiffness in Marfan syndrome
Ami B Bhatt, J Stewart Buck, Jonah P Zuflacht, Jessica Milian, Samoneh Kadivar, Kimberlee Gauvreau, Michael N Singh, Mark A Creager
Vascular Medicine.2015; 20(4): 317. CrossRef - The impact of angiotensin receptor blockers on arterial stiffness: a meta-analysis
Feng Peng, Hongming Pan, Bin Wang, Jinxiu Lin, Wenquan Niu
Hypertension Research.2015; 38(9): 613. CrossRef - Arterial stiffness in atherosclerotic renovascular hypertension
Ljiljana Fodor, Vedran Premužić, Vanja Ivković, Dražen Perkov, Mario Laganović, Tajana Željković Vrkić, Živka Dika, Marijana Živko, Bojan Jelaković
Journal of Hypertension.2014; 32(11): 2238. CrossRef - Improvement of arterial wall characteristics by the low-dose fluvastatin and valsartan combination in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients
Vedran Savić, Barbara Eržen, Miodrag Janić, Mojca Lunder, Maja Boncelj, Karin Kanc, Andrej Janež, Mišo Šabovič
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2013; 10(5): 420. CrossRef - The association between regional arterial stiffness and diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes
Won Jun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Won Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Sun Woo Kim, SuJeong Song
Atherosclerosis.2012; 225(1): 237. CrossRef - Letter: The Effect of an Angiotensin Receptor Blocker on Arterial Stiffness in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Hypertension (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:236-42)
Chul-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 427. CrossRef
- Mechanisms underlying the blood pressure‐lowering effects of empagliflozin, losartan and their combination in people with type 2 diabetes: A secondary analysis of a randomized crossover trial
- The Usefulness of an Accelerometer for Monitoring Total Energy Expenditure and Its Clinical Application for Predicting Body Weight Changes in Type 2 Diabetic Korean Women
- Ji Yeon Jung, Kyung Ah Han, Hwi Ryun Kwon, Hee Jung Ahn, Jae Hyuk Lee, Kang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(6):374-383. Published online December 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.6.374
- 7,710 View
- 24 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of an accelerometer in predicting body weight (BW) change during a lifestyle intervention and to find out whether exercise or overall physical activity is associated with change in insulin sensitivity and body composition.
Methods A total of 49 overweight (body mass index [BMI] ≥ 23 kg/m2) women with diabetes were enrolled and performed lifestyle intervention while monitoring BW, total energy expenditure (TEE) and physical activity energy expenditure (PAEE) using an accelerometer, and energy intake (EI) using a three-day dietary record at baseline and every 2 weeks for 12 weeks. We assessed body composition using bioimpedance analysis and compared the actual BW change to the predicted BW change, which was calculated from the energy deficit (ED) between EI and TEE (ED = EI-TEE).
Results Mean age was 57.2 years, duration of diabetes was 8.0 years, and BMI was 27.8 kg/m2. There was no significant difference between EI and TEE at baseline. For 12 weeks, the ED was 474.0 kcal·day-1, which was significantly correlated with BW change (-3.1 kg) (
r = 0.725,P < 0.001). However, the actual BW change was 50% lower than the predicted BW change. Both TEE and PAEE correlated with change in KITT (r = 0.334,P = 0.019;r = 0.358,P = 0.012, respectively), BMI (r = -0.395,P = 0.005;r = -0.347,P = 0.015, respectively), and fat mass (r = -0.383,P = 0.007;r = -0.395,P = 0.005, respectively), but only TEE correlated with fat free mass change (r = -0.314,P = 0.030).Conclusion The accelerometer appears to be a useful tool for measuring TEE under free-living conditions for both short- and long-term periods.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Whether Smaller Plates Reduce Consumption Depends on Who’s Serving and Who’s Looking: A Meta-Analysis
Stephen S. Holden, Natalina Zlatevska, Chris Dubelaar
Journal of the Association for Consumer Research.2016; 1(1): 134. CrossRef
- Whether Smaller Plates Reduce Consumption Depends on Who’s Serving and Who’s Looking: A Meta-Analysis
- The Small Rice Bowl-Based Meal Plan was Effective at Reducing Dietary Energy Intake, Body Weight, and Blood Glucose Levels in Korean Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hee Jung Ahn, Kyung Ah Han, Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Wan Min
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(6):340-349. Published online December 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.6.340
- 3,256 View
- 34 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The typical Korean diet includes rice, which is usually served in a rice bowl. We investigated the effects of a meal plan using rice bowls of varying sizes on dietary energy intake (EI), body weight (BW), and blood glucose levels.
Methods Forty-two obese women with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomly assigned to use either a 200 mL small rice bowl (SB), a 380 mL regular rice bowl (RB), or to a control group (C). Both intervention groups were asked to reduce their EI by 500 kcal/day for 12 weeks and simple instructions for using the assigned bowl were provided. Dietary EI and proportion of macronutrients (PMN) were estimated from 3-day dietary records.
Results Reduction of EI was more prominent in the SB group compared to the RB and C group, although EI decreased significantly from baseline in all groups. Carbohydrate and fat intakes of the SB group were decreased greater than those of the RB and C group. However, changes in PMN were not significant across the 3 groups. Reduction of BW and HbA1c levels in the SB group was more prominent compared to the C group. Although, BW and HbA1c were decreased significantly from baseline in both bowl groups. There was no statistical difference between the two groups.
Conclusion The small rice bowl-based meal plan was effective at reducing EI, BW, and blood glucose levels, and the observed reductions in EI, carbohydrate, and fat intake were greater than those of the regular rice bowl-based meal plan.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Portion Control Tools on Portion Size Awareness, Choice and Intake: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
M. Angeles Vargas-Alvarez, Santiago Navas-Carretero, Luigi Palla, J. Alfredo Martínez, Eva Almiron-Roig
Nutrients.2021; 13(6): 1978. CrossRef - Do adults draw differently-sized meals on larger or smaller plates? Examining plate size in a community sample
David Sharp, Jeffery Sobal, Elaine Wethington
Food Quality and Preference.2019; 74: 72. CrossRef - Use and effectiveness of behavioural economics in interventions for lifestyle risk factors of non-communicable diseases: a systematic review with policy implications
Oana M Blaga, Livia Vasilescu, Razvan M Chereches
Perspectives in Public Health.2018; 138(2): 100. CrossRef - Whether Smaller Plates Reduce Consumption Depends on Who's Serving and Who's Looking: A Meta-Analysis
Stephen S. Holden, Natalina Zlatevska, Chris Dubelaar
SSRN Electronic Journal .2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Portion, package or tableware size for changing selection and consumption of food, alcohol and tobacco
Gareth J Hollands, Ian Shemilt, Theresa M Marteau, Susan A Jebb, Hannah B Lewis, Yinghui Wei, Julian P T Higgins, David Ogilvie
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of Portion Control Tools on Portion Size Awareness, Choice and Intake: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





